Python
1. Python is an interpreted high-level programming language for general-purpose programming.
2.To interact with Python shell -> Start IDLE
3. >>> <- is the Python shell prompt. Marks a line of input from the user, while lines without are generated by Python.
4. Transcript -> a shell transcript is a snapshot of the command shell showing a series of user inputs and Python replies.
5. Command shell is often abbreviated a interactive shell, command shell, shell or even command line.
6.Python has an integer division operator, //. Works like /, except always returns an integer. Ex. 7//2 will be 2. (// does not round.)
7. Name Operator Example
addition + >>>3+4 ->7
subtraction - >>> 5-3 ->2
multiplication * >>> 2*3 ->6
division / >>>3/2 ->1.5
integer division // >>> 3//2 ->1
remainder % >>> 25%3 ->1
exponentiation ** >>>3**3 ->27
8. Python put no limit on the size of an integer.
>>> 27**100
13689147905858837....
9. Floating Point Arithmetic. For example -3.1; 2.999 or -4.0 called FLOATS for short.
10. Floating numbers have minimum and maximum value, that if exceeded, will cause overflow error
>>>5000**10000 is too large to store as a float.
11. Silent error is when Python does calculation incorrectly without telling that anything bad has happened.
RGB Colours
1.White - is a mixture of colours
2.RGB - is a colour code which stands for RED, GREEN and BLUE.
3.Picture on the right shows 8-bit RGB colours.


Image Sensor
Is a sensor that detects and conveys the information that constitutes an image.'
Types :
* CMOS
New design
Cheaper
Widely used
Scans in Rows (Rolling Shutter)
* CCD
Older
Expensive
Scans everything at once (Global Shutter)
Major Compressed Image Formats:
-
JPEG
-
PNG
-
GIF
Dynamic Range

First Python Exercises:
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |


This exercise was to explore, how picking up different alpha values the colour changes in the 'Shark' picture is changing.
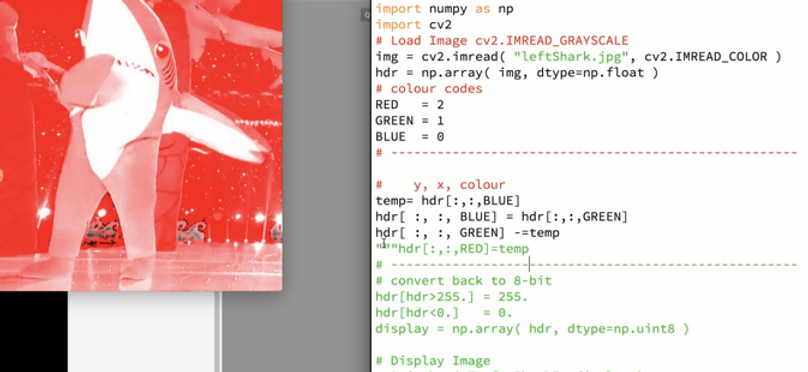


To create staircase :
import maya.cmds as mc
step_w = 85
step_h = 12
step_d = 18
of_y = step_h
of_z = step_d-1
height = 360
num_steps = height / step_h
for i in range (num_steps):
mc.polyCube(w=step_w, h=step_h, d=step_d, n="step1")
mc.move(0.1*of_y, i*of_z, a=True)
Challenge 1: Make the Railings

Challenge 2: Random Grass Script


NUKE : Camera Tracking basics


Firstly, we upload our video, that we want to track. Creating a Camera Tracker by pressing TAB button in a blank area. When we created the Camera Tracker, we selected the Viewer1 and On the Read1, we pressed number 1 and on Camera Tracking number 2.





The main was was to create a chequer board to stick on the wall. Tat is why, we created Card1 by using quick TAB button, attached it to our Scene1 and connected 'img' node to it.

